How to send notifications to users of the Farcaster Mini App
This guide walks you through how you can send notifications to your Mini App users.
This guide uses Monad Mini App template, which already has the code for sending notifications; all you have to do is modify a few lines of code.
If you aren't using the template, you can still follow the guide; feel free to copy code as needed from the template.
Demo
If you want to try the Mini App notification experience, you can try the Monad Mini App Template app.
Modifying the Mini App manifest
Mini App account association process has to be completed before the Mini App can send notifications.
Mini Apps can send notifications to the user when:
- The user has added the Mini App and not disabled notifications manually
- The user has explicitly subscribed to notifications from the Mini App
Farcaster app or clients send events like miniapp_added, miniapp_removed, notifications_disabled and notifications_enabled to the Mini App's webhook endpoint, this allows the Mini App to keep track of which users the Mini App can send notifications to.
The webhookUrl has to be specified in the Mini App manifest file:
...
export async function GET() { const farcasterConfig = { // TODO: Add your own account association frame: { version: "1", name: "Monad Farcaster Mini App Template", ... splashBackgroundColor: "#ffffff", webhookUrl: `${APP_URL}/api/webhook`, // <--- Edit this },};
...If you are using the Monad Mini App Template, you don't need to edit the webhookUrl.
Processing Farcaster client events
The code for processing webhook events can be found in the file /app/api/webhook/route.ts.
Verifying webhook events
Events are signed by the app key of a user with a JSON Farcaster Signature. This allows Mini Apps to verify the Farcaster client that generated the notification and the Farcaster user they generated it for.
It is important to verify events in order to make sure the Mini App is correctly tracking which users it can send notifications to.
If you are using the Monad Mini App template, the code for verifying events is already available in /app/api/webhook/route.ts. If not, you can copy code from the same file.
A Neynar API key is required to verify webhook events. You can sign up to the Neynar service and get an API key for free.
Once done, add a environment variable named NEYNAR_API_KEY to your .env file.
Processing webhook payload
Once the webhookUrl is specified, Farcaster app and clients will send client events to the webhook endpoint.
The miniapp_added and notifications_enabled events are received by the Mini App along with fid and notificationDetails.
notificationDetails has a url and a token that can be used to send notifications to a specific Farcaster user.
Example of webhook payload:
{ "fid": 17979, "event": { "event": "notifications_enabled", "notificationDetails": { "url": "https://api.farcaster.xyz/v1/frame-notifications", "token": "a05059ef2415c67b08ecceb539201cbc6" } }}You can find the code, handling the Farcaster client events in /app/api/webhook/route.ts.
The Mini App can use any database service of choice to store the url and token and use it when sending notifications.
The Monad Mini App template uses Upstash's Redis service for storing the notificationDetails, if you wish to use a different database you can modify it in /lib/kv.ts.
Since the Monad Mini App template uses Redis for storing notification url and token, environment variables UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL and UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN are required in .env.
Once you sign up for the Upstash service and create a Redis database you will be able to get these environment variables.
If you plan to use some other database, adjust environment variables accordingly.
Example of storing notification details in Redis:
...
const redis = new Redis({ url: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_URL, token: process.env.UPSTASH_REDIS_REST_TOKEN,});
...
export async function setUserNotificationDetails( fid: number, notificationDetails: MiniAppNotificationDetails): Promise<void> { // Modify lines that use redis to use your own database implementation await redis.set(getUserNotificationDetailsKey(fid), notificationDetails); }
...Sending notifications
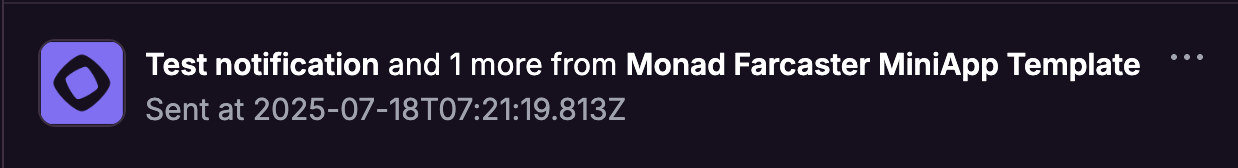
Once you have a notification token for a user, you can send them a notification by sending a POST request to the url associated with that token.
If you are using the Monad Mini App template the code for sending notification is already available in the file /app/api/send-notification/route.ts. If not, you can copy code from /lib/notifs.ts and /app/api/send-notification/route.ts.
Personalizing notification content
You can change a few lines of code in /app/api/send-notification/route.ts file to personalize the notification:
...
// This function sends the notificationconst sendResult = await sendFrameNotification({ fid: requestBody.data.fid, // You can modify/personalize the below line to make the title of the notification dynamic based on the fid (user) title: "Test notification", // You can modify/personalize the below line to make the body of the notification dynamic based on the fid (user) body: "Sent at " + new Date().toISOString(),});
...Notification Rate Limits
The standard rate limits, which are enforced by Farcaster, are:
- 1 notification per 30 seconds per token
- 100 notifications per day per token
If you are using the Monad Mini App template, you can send notifications from the server or the Mini App by making a POST to /api/send-notification endpoint!
That's all you need to send notifications to your Mini App users!